Oracle AWR (Automatic Workload Repository) is the de facto standard for performance analysis in Oracle Database Enterprise Edition (EE).
Integrated at the kernel level as the successor to Statspack, it automatically collects operation statistics with greater detail and lower overhead.
This article explains the procedure for generating AWR reports, how to change settings, and the decisive difference from Statspack (license requirements), targeting an Oracle Database 26ai environment.
Conclusion: AWR is “Auto-Collection, Manual Output”
Let’s summarize the conclusion and key points first.
- Key Feature: Enabled by default (auto-collection every 60 minutes). Ready to use without configuration.
- Prerequisite: Enterprise Edition and Diagnostics Pack (paid option) are mandatory for production use.
- Shortest Path (Report Output):
- Run
@?/rdbms/admin/awrrptin SQL*Plus. - Select the target number of days and snapshot IDs.
- Decide the output format (HTML recommended) and file name.
- Run
- If you are told, “Performance trouble! Get the report!”, first execute the steps in this article.
What is AWR? Difference from Statspack
Overview of AWR (Automatic Workload Repository)
This is an automatic workload repository introduced in Oracle Database 10g. It automatically accumulates DB operation statistics (wait events, SQL statistics, OS statistics, etc.) in the SYSAUX tablespace.
Comparison Table with Statspack
| Item | AWR (Automatic Workload Repository) | Statspack |
| Target Edition | Enterprise Edition (Requires Option) | Standard Edition / EE / Free |
| License | Diagnostics Pack is mandatory | No additional cost |
| Data Collection | Automatic by default (60 min interval) | Manual config required (JOB registration) |
| Data Precision | Very High (Includes ASH details, etc.) | Standard |
| Interface | HTML Report / EM Cloud Control | Text Report only |
Professional Note (License)
AWR is very powerful, but using it in an environment where the Diagnostics Pack license has not been purchased constitutes a license violation. You can control usage with the control_management_pack_access parameter. In Standard Edition (SE2) environments, use Statspack in principle.
Note: In developer license versions such as Oracle Database 26ai Free, usage is permitted for learning and development purposes.
Step 1: Checking and Changing AWR Settings
AWR is enabled by default, but the interval or retention period may be changed depending on the site.
In a multitenant environment, you can check the setting status of each container by using the CDB_HIST_WR_CONTROL view.
Check Current Settings
Check the CDB_HIST_WR_CONTROL view.
COL snap_interval FORMAT a20
COL retention FORMAT a25
SELECT dbid, con_id, snap_interval, retention, topnsql
FROM cdb_hist_wr_control;
- SNAP_INTERVAL: Snapshot collection interval (Default:
+00 01:00:00.000000= 1 hour) - RETENTION: Data retention period (Default:
+00 08:00:00.000000= 8 days)
SQL> COL snap_interval FORMAT a20
SQL> COL retention FORMAT a25
SQL> SELECT dbid, snap_interval, retention, topnsql
2 FROM dba_hist_wr_control;
DBID SNAP_INTERVAL RETENTION TOPNSQL
---------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----------
1491844267 +00000 01:00:00.0 +00008 00:00:00.0 DEFAULT
Change Settings (Example: 15-minute interval, 30-day retention)
During troubleshooting, you might shorten the interval. Use the DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPOSITORY package to make changes.
BEGIN
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPOSITORY.MODIFY_SNAPSHOT_SETTINGS(
retention => 43200, -- Minutes (30 days = 30 * 24 * 60 = 43200)
interval => 15 -- Minutes (15 minutes)
);
END;
/
SQL> BEGIN
2 DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPOSITORY.MODIFY_SNAPSHOT_SETTINGS(
3 retention => 43200,
4 interval => 15
5 );
6 END;
7 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> COL snap_interval FORMAT a20
SQL> COL retention FORMAT a25
SQL> SELECT dbid, con_id, snap_interval, retention, topnsql
2 FROM cdb_hist_wr_control;
DBID CON_ID SNAP_INTERVAL RETENTION TOPNSQL
---------- ---------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----------
1266666428 3 +00000 00:15:00.0 +00030 00:00:00.0 DEFAULT
Check Captured Snapshots
SQL to check if AWR is operating normally or to confirm the IDs for report output in advance.
-- Display snapshots
SELECT snap_id, begin_interval_time, end_interval_time
FROM dba_hist_snapshot
ORDER BY snap_id;
SQL> SELECT snap_id, begin_interval_time, end_interval_time
2 FROM dba_hist_snapshot
3 ORDER BY snap_id;
SNAP_ID BEGIN_INTERVAL_TIME END_INTERVAL_TIME
---------- ----------------------------------- -----------------------------------
3 20-JAN-26 09.58.40.750 PM 20-JAN-26 10.58.50.765 PM
4 20-JAN-26 10.58.50.765 PM 20-JAN-26 11.58.55.371 PM
5 20-JAN-26 11.58.55.371 PM 21-JAN-26 12.58.59.753 AM
6 21-JAN-26 12.58.59.753 AM 21-JAN-26 01.58.11.061 AM
7 21-JAN-26 01.58.11.061 AM 21-JAN-26 02.58.16.354 AM
8 21-JAN-26 02.58.16.354 AM 21-JAN-26 03.58.20.947 AM
9 21-JAN-26 03.58.20.947 AM 21-JAN-26 04.58.25.506 AM
10 21-JAN-26 04.58.25.506 AM 21-JAN-26 05.58.30.321 AM
11 21-JAN-26 05.58.30.321 AM 21-JAN-26 06.58.35.341 AM
12 21-JAN-26 06.58.35.341 AM 21-JAN-26 07.58.39.816 AM
13 21-JAN-26 07.58.39.816 AM 21-JAN-26 08.58.44.294 AM
14 21-JAN-26 08.58.44.294 AM 21-JAN-26 09.58.48.911 AM
15 21-JAN-26 09.58.48.911 AM 21-JAN-26 10.58.53.551 AM
16 21-JAN-26 10.58.53.551 AM 21-JAN-26 11.58.57.940 AM
17 21-JAN-26 11.58.57.940 AM 21-JAN-26 12.58.02.504 PM
18 21-JAN-26 12.58.02.504 PM 21-JAN-26 01.58.07.398 PM
19 21-JAN-26 01.58.07.398 PM 21-JAN-26 02.58.12.112 PM
20 21-JAN-26 02.58.12.112 PM 21-JAN-26 03.58.16.939 PM
21 21-JAN-26 03.58.16.939 PM 21-JAN-26 04.58.21.754 PM
22 21-JAN-26 04.58.21.754 PM 21-JAN-26 05.58.26.436 PM
23 21-JAN-26 05.58.26.436 PM 21-JAN-26 06.58.31.129 PM
24 21-JAN-26 06.58.31.129 PM 21-JAN-26 07.58.35.578 PM
25 21-JAN-26 07.58.35.578 PM 21-JAN-26 08.58.39.987 PM
23 rows selected.
Step 2: Creating an AWR Report (awrrpt.sql)
This is the most frequent operation. Run an interactive script in SQL*Plus.
1. Run Script
Connect to the analysis target database (or target PDB in a CDB environment) with a user having SYS or DBA privileges and run the script.
-- If you want to output a PDB report, connect to the PDB before execution
CONN / AS SYSDBA
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER = FREEPDB1;
-- Set specifically for HTML output readability
SET PAGES 0 LINES 200
-- Execute report generation script
@?/rdbms/admin/awrrpt
2. Interactive Input
Upon execution, you will be prompted for input in the following order:
- report_type: Report format. You can select
htmlortext. We recommendhtml, which can be viewed in a browser and is color-coded for readability. - num_days: Number of days of snapshots to display. Enter
1for the most recent, or3for three days ago. - begin_snap: Select and enter the Snap Id from the list for the start of the investigation.
- end_snap: Enter the Snap Id for the end of the investigation.
- report_name: Output file name. Press Enter if the default is fine (e.g.,
awrrpt_1_100_101.html).
3. Check Report
An HTML file is generated in the current directory. Open it in a browser to see a graphical, color-coded report.
Point:
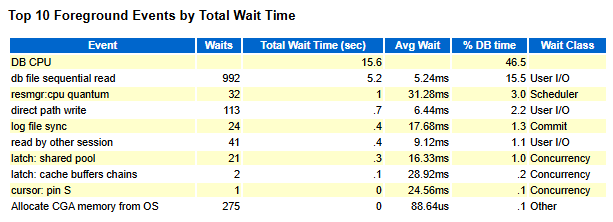
The “Top 10 Foreground Events by Total Wait Time” section is the most important. You can see at a glance what the DB was spending time on.
AWR in Multitenant (CDB/PDB) Environments
Since Oracle 12c, AWR operates at both the CDB level and the PDB level.
- Whole CDB (CDB$ROOT): Used when looking at the load of the entire instance. Execute
awrrpt.sqlin the root container. - Individual PDB: Used when looking at the load of a specific tenant. In 26ai environments, snapshots per PDB are also automatically collected by default.
When outputting an AWR report for a PDB, ensure you switch to the target PDB using ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER before executing awrrpt.sql.
Troubleshooting: Common Errors and Solutions
Q. Snapshots are not being automatically generated
Cause: The STATISTICS_LEVEL parameter might not be set to TYPICAL (default) or ALL.
Check:
SHOW PARAMETER statistics_level
-- If set to BASIC, AWR stops
Q. SYSAUX tablespace has become bloated
Cause: The AWR retention period (RETENTION) is too long, or the volume of SQL statistics is too high.
Solution: Shorten the retention period (e.g., return to 8 days) or manually purge old snapshots.
-- To return settings to default (Retention: 8 days, Interval: 60 mins)
BEGIN
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPOSITORY.MODIFY_SNAPSHOT_SETTINGS(
retention => 11520, -- 8 days (Minutes: 8*24*60)
interval => 60 -- 60 minutes
);
END;
/
-- Example of manual purge (Deleting IDs: 100 to 110)
BEGIN
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPOSITORY.DROP_SNAPSHOT_RANGE(
low_snap_id => 100,
high_snap_id => 110
);
END;
/
Q. “ORA-13516: AWR Operation failed: CATWRUP not run”
Cause: Occurs when internal schemas for AWR have not been updated, such as after a database upgrade.
Solution: Verification is required to ensure upgrade processes via catupgrd.sql etc., have completed normally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. How do I check AWR data capacity?
Check the size of AWR-related objects within the SYSAUX tablespace. You can get an estimate with the following SQL:
SELECT OCCUPANT_NAME, SPACE_USAGE_KBYTES/1024 AS MB
FROM V$SYSAUX_OCCUPANTS
WHERE OCCUPANT_NAME LIKE 'SM%';
Q. What if I want to see the detailed history of a specific SQL only?
Use the SQL detailed report (awrsqrpt.sql) instead of the standard AWR report (awrrpt.sql). By specifying the SQL ID, you can output the transition of execution plans and statistics for that SQL in detail.
Q. What is the overhead of AWR collection?
Since AWR reads statistical information directly from memory from within the Oracle Database kernel, the overhead is very low compared to Statspack (which collects via SQL). It is rare for AWR collection processes to become a bottleneck in normal operations.
Summary
- AWR requires Enterprise Edition + Diagnostics Pack. Be strictly careful about license violations.
- Enabled by default. The ability to check past data without configuration changes is a strength over Statspack.
- For report output, just remember
@?/rdbms/admin/awrrpt. - In multitenant environments, be conscious of the distinction between Whole CDB and Individual PDB.
Understand the characteristics and license requirements of Statspack and AWR respectively, and select the optimal tool for your environment.
[reference]
Oracle AI Database Database Performance Tuning Guide, 26ai
This article explains the topic targeting Oracle Database 26ai. The verification for this article was conducted on the 26ai Free version, so specifications or default values may differ slightly when the formal version (Enterprise Edition, etc.) is released.



コメント